Since Facebook was renamed Meta, a lot of attention, debate, and exploration has intensified about what the Metaverse is, how it works, and possible ways to exploit it.
The Metaverse is expected to be a rapidly emerging continuum of technologies, use cases, capabilities and experiences that will complement the next evolution of the Internet.
To this end, a comprehensive and in-depth review of AI, 6G, and the role of both in enabling an immersive experience in the Metaverse is presented from Southeastern University of Technology in Ireland.
picture
Paper address: https://arxiv.org/abs/2208.10921
First, the author introduces the background and progress of Augmented Reality (AR), Virtual Reality (VR), Mixed Reality (MR) and spatial computing, and then introduces the technical aspects of AI and 6G. The authors then investigate the role of AI in the metaverse by reviewing the state-of-the-art in deep learning, computer vision, and AI at the edge.
Next, the author investigates the promising services of B5G/6G for the Metaverse, and then determines the role of AI in the 6G network and the role of AI in supporting the application of the Metaverse in the 6G network. Finally, the authors describe existing and potential applications, use cases, and projects to highlight the importance of progress in the metaverse.
Furthermore, to provide researchers with potential research directions, the authors enumerate challenges, research gaps, and lessons learned from a literature review of the aforementioned techniques.
introduction
In 2021, the Metaverse begins to impact the real world due to: i) the pandemic lifestyle, and ii) Meta, Amazon, Apple, Netflix and Google (MAANG) releasing Metaverse related features and projects for their users.
Since then, the Metaverse has garnered absolute attention from both academia and industry. At the current point in time, the metaverse can be universally viewed as a pool of extended reality (XR) space in which humans and their digital counterparts interact in a fully immersive way.
According to a recent survey, most technologists believe that by 2040, the Metaverse will function more fully and seamlessly, and people around the world will be able to fully participate in its fully immersive capabilities as part of their daily lives. a component.
Essentially, the Metaverse is expected to integrate all important aspects of cyberspace or the World Wide Web, such as B5G/6G, cloud and edge computing, social media, online gaming, augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), cryptocurrencies And artificial intelligence (AI)/machine learning (ML)/deep learning (DL) platforms and applications that allow users to interact virtually.
Some early applications of the Metaverse, such as Roblox, VRChat, Zepeto or Second Life, have allowed users to live “different” or simulated lives, such as making friends and socializing with new virtual characters. These platforms already have AR, VR and MR as several elements of the metaverse.
Virtual reality is the use of various software and communication devices such as head-mounted displays (HMDs) to replace the real world around the user with computer-generated digital scenes. In AR, the virtual world is seamlessly connected with the real world to create new interactive experiences. Finally, MR emerged as a combination of AR and VR and their underlying technologies.
It is worth noting that the proliferation of these technologies has made AR and VR devices available at affordable prices while continuously improving the quality of user experience (QoE).
However, in order to achieve the processing power and communication speed required by VR services to provide a smooth and immersive experience, most HMDs still require users to connect to a PC or gaming console. The only device that can break free from this shackles is Meta’s Oculus Quest. Over the next few years, as processors become faster and wireless communication technology becomes lag-free, there will be many improvements to visual content and the connectionless experience of mobile devices.
With 5G in particular, there will be a proliferation of devices connected to the network, which will have profound implications for the growth of the metaverse. 5G enables real-time communication and information exchange between all connected devices with low latency.
Obviously, 5G offers faster speeds than 4G, but most importantly, it offers a variety of other benefits beyond speed. Specifically, Metaverse developers will be able to benefit from 5G’s low latency by creating applications that stream 360◦ content in near real-time.
The Metaverse will also foster the trend towards human-centric/data-centric intelligent systems. This trend imposes many limitations on existing 5G communication systems, making them less efficient and unreliable.
For example, given the 0.1ms latency requirements of haptic-based metaverse applications such as teleportation or teleoperation, 5G can only provide air interface latency of less than 1ms, which is insignificant for such an application.
Additionally, according to Cisco, mobile data traffic has grown 17-fold over the past five years and is expected to continue to grow. In particular, 5G traffic will account for 12% of total global mobile traffic by 2022.
5G networks are designed to cover large areas of spectrum, such as millimeter wave (up to 300 GHz), so they can handle large amounts of wireless traffic.
Since the Metaverse will bring some applications that may require higher than Tbps data rates, which is less likely to be the case with mmWave systems, such as Holographic Presence (HT), Haptic Sensory Communication, Brain-Computer Interface (BCI) and XR . Therefore, in order to achieve the goal of Tbps data rate, researchers began to explore the terahertz (THz) frequency band (0.1-10 THz).
The 6G communication system is expected to provide a data rate of 1Tbps and run at a bandwidth of 3Thz to support data-intensive applications such as online games, high-definition video live broadcast, holographic content transmission, and real-time avatar interaction. 6G will also provide ubiquitous coverage and ultra-low latency (less than 1ms), and support maneuvering capabilities of around 100 km/h by integrating space, air, ground, and ocean networks.
However, Metaverse applications such as virtual education and training, precise navigation and positioning, immersive gaming, and telemedicine applications will all be enabled by AI and 6G, making the Metaverse more successful. In particular, cutting-edge techniques in computer vision can be used to provide 3D animated mannequins or lifelike animated faces, and even to create holograms.
However, a key challenge in using 3D content for metaverse services lies in the scalability of existing infrastructure. As such, the rise of the Metaverse makes it critical to develop key tools and infrastructure to enable Metaverse developers to build better and more scalable 3D/AR/VR experiences regardless of platform or purpose.
In principle, researchers need to take a step away from the supervised learning paradigm of AI and employ diverse learning strategies such as reinforcement learning and self-supervised learning to scale in the metaverse setting. In addition, the edge computing capabilities of 6G networks can be combined with AI to provide edge intelligence, thereby reducing network latency and privacy issues with enhanced QoE in the Metaverse.
Driven by existing technologies and foreseeable challenges, the authors survey the state-of-the-art in AI and 6G in the context of metaworlds to answer the following questions: How can AI, 6G, and the continued progress between the two be leveraged to provide better and sustainable metaworld experiences?
It is clear from the above discussion that some of the existing investigations focus on a very narrow view of AI, 6G and related technologies, while others investigate the role of the metaverse in terms of social, economic and digital value. In contrast, in this review, the authors provide the following key contributions:
The authors describe the underlying components of the metaverse, namely VR, MR, AR, and spatial computing. This article presents the detailed background of the above technologies so that the reader understands the technical aspects and state-of-the-art technology to enable a fully immersive metaverse.
The authors provide an extensive review of the state-of-the-art in artificial intelligence and examine the role of artificial intelligence in realizing the metaverse. Essentially, the authors define the role of AI in the layered architecture of the metaverse, followed by state-of-the-art for computer vision applications, learning paradigms, and edge AI in the metaverse.
The authors explain the role of B5G/6G in enabling the metaverse by first answering the following key questions: i) Will B5G/6G take an hour? ii) What services can B5G/6G bring to the metaverse? Next, by specifically considering 5G-NR, URLLC, mmWave, MEC, thzcomm, and their interplay, the authors review the state-of-the-art in immersive experiences and wireless holographic telepresence.
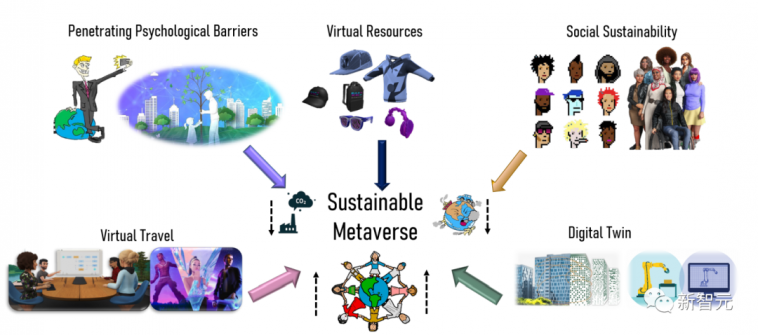
The authors also consider the combined role of AI and 6G in enabling the metaverse. In principle, the authors investigate the potential of AI for 6G networks and 6G networks for AI to support the metaverse. Next, the authors will investigate the sustainability of the metaverse in the aforementioned technical context, followed by potential applications and use cases and ongoing projects. Finally, the authors present challenges and future research directions as well as lessons learned from this survey.
picture
The term “Metaverse” is a combination of the prefix “meta” (meaning “transcendence”) and the suffix “verse” (short for “universe”). Hence, it refers to the universe beyond the physical world. This “beyond the universe” alludes to a computer-generated environment, not a metaphysical or mystical conceptual realm beyond physical reality.
The Metaverse is a fully immersive three-dimensional digital environment, unlike cyberspace, which refers to all online spaces.
picture
The metaverse refers to the transformation of physical reality into the digital realm, so it can be a mix of physical reality and digital realm, such as AR, VR, MR.



GIPHY App Key not set. Please check settings