Scientists at Johannes Kepler University in Austria have recently developed a steerable soft robot that can run, swim and jump at high speed. During the test, the robot reached a running speed of 70 times its body length per second. The result is amazing. Yes, because even a cheetah (the fastest land animal on Earth) can only reach a speed of 23 times its body length per second!
Comparable to the robot “Little Cheetah”
While they may be the fastest soft robots on the planet, one shouldn’t expect them to hit absolute speed records because the robot’s body is only millimeters in size. Soft robots are different from the traditional robots seen in factories, restaurants and science fairs, which are made of flexible materials such as polymers and shape memory alloys (which change shape with temperature) that make the robots more functional. Functionally similar to living organisms or living tissue, conventional robots are made of rigid materials such as plastic, aluminum and metal.
Scientists have long tried to create soft robots that are fast enough to operate in extreme environments where other machines cannot. They could play an important role in the medical field, for example: ultrafast robots could replace invasive procedures such as colonoscopy In this way, doctors can use the ultra-fast soft robot to check for abnormalities in any body organ that is difficult for traditional diagnostic robots to examine, such as the stomach.
super speed robot
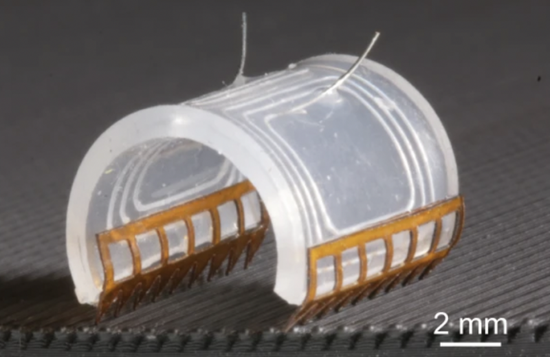
This super-speed robot is made of a liquid metal alloy called galinstan, which is composed of tin, gallium and indium elements. Galinstan is usually not used to make soft robots. Soft robots are generally made of silicon-based elastic materials. “The most important property of this material is that it is liquid at room temperature and also has high electrical conductivity,” said first author of the study, Dr. Mao Guoyong, a soft matter physicist at Johannes Kepler University. This will help create soft, deformable coil structures.”
The researchers used liquid metal 3D printing to fabricate galinstan coils, which are embedded in elastic shells, using an actuator to control their shape, resulting in a coil-like soft electromagnetic robot (SEMR) capable of providing rapid actuation and propulsion , the researchers were equipped with L-shaped or zigzag-shaped “feet” depending on the base the robot moved.
Soft electromagnetic robots are powered by lithium polymer batteries, and their ultra-fast movements are driven by electromagnetic actuators (components that convert electrical energy into mechanical energy), which are magnetically responsive elements, so fast-moving robots can be easily performed using static magnetic fields. control. During testing, the tethered robots traveled at 35 times their body length per second on airplanes and 70 times their body lengths per second on the surface of a 3D folded object. In addition, in underwater tests, their The swimming speed is 4.8 times body length per second. Mao Guoyong pointed out that we think this is a promising new technology in the field of robotics, with great potential in the future, we cannot find any similar technology, using a soft functional material, can complete many things at very high speed. Task.
The Future of Speeding Robots
At the same time, the researchers also conducted speed tests on prototypes of tethered soft robots. The results showed that their swimming speed was 1.8 times their body length per second, and their maximum land movement speed was 2.1 times their body length per second. The efficiency and performance of tethered robots.
Mao Guoyong and his colleagues said that the use of liquid 3D printing technology to develop more millimeter-scale soft electromagnetic robots will help to manufacture larger super-speed soft robots in the future.
In recent years, scientists have devoted themselves to the development of soft robots, and many types of soft robots have emerged. Some soft robots can help us remove plastic waste from the ocean, while others allow us to study and analyze the high-temperature deserts on the surface of the moon and Mars. For all soft robots, speed is a big limiting factor, and ultra-fast soft electromagnetic robotics technology may break through this bottleneck.



GIPHY App Key not set. Please check settings